Folding@home (FAH or F@h) is a
distributed computing project aimed to help scientists develop new therapeutics to a variety of diseases by the means of simulating protein dynamics. This includes the process of protein folding and the movements of proteins, and it's all reliant on the simulations run on the volunteers' personal computers.
[4] Folding@home is currently based at
Washington University in St. Louis and led by Dr. Greg Bowman, a former student of Dr. Pande.
[5]
The project has pioneered the utilization of
central processing units (CPUs),
graphics processing units(GPUs),
PlayStation 3s,
Message Passing Interface(used for computing on
multi-core processors), and some
Sony Xperia smartphones for distributed computing and scientific research. The project uses statistical
simulation methodology that is a
paradigm shift from traditional computing methods.
[6] As part of the
client–server model network architecture, the volunteered machines each receive pieces of a simulation (work units), complete them, and return them to the project's
database servers, where the units are compiled into an overall simulation. Volunteers can track their contributions on the Folding@home website, which makes volunteers' participation competitive and encourages long-term involvement.
Folding@home is one of the world's fastest computing systems. With heightened interest in the project as a result of the
2019–20 coronavirus pandemic, the system achieved a speed of approximately 1.22
exaFLOPS by late March 2020 and reaching 2.43 x86 exaFLOPS by April 12, 2020,
[7] making it the world's first
exaFLOP computing system. This level of performance from its large-scale computing network has allowed researchers to run
computationally costly atomic-level simulations of protein folding thousands of times longer than formerly achieved. Since its launch on 1 October 2000, the Pande Lab has produced 223
scientific research papers as a direct result of Folding@home.
[8] Results from the project's simulations agree well with experiments.
[9][10][11]
Contents
1Background
2Examples of application in biomedical research
2.1Alzheimer's disease
2.2Huntington's disease
2.3Cancer
2.4Osteogenesis imperfecta
2.5Viruses
2.6Drug design
3Potential applications in biomedical research
3.1Prion diseases
4Patterns of participation
4.1Performance
4.2Points
5Software
5.1Work units
5.2Cores
5.3Client
5.3.1Graphics processing units
5.3.2PlayStation 3
5.3.3Multi-core processing client
5.3.4V7
5.3.5Google Chrome
5.3.6Android
6Comparison to other molecular simulators
7See also
8References
9Sources
10External links
Background[
edit]
Further information:
Protein folding

A protein before and after folding. It starts in an unstable
random coil state and finishes in its native state conformation.
Proteins are an essential component to many biological functions and participate in virtually all processes within
biological cells. They often act as
enzymes, performing biochemical reactions including
cell signaling, molecular transportation, and
cellular regulation. As structural elements, some proteins act as a type of
skeleton for cells, and as
antibodies, while other proteins participate in the
immune system. Before a protein can take on these roles, it must fold into a functional
three-dimensional structure, a process that often occurs spontaneously and is dependent on interactions within its
amino acid sequence and interactions of the amino acids with their surroundings. Protein folding is driven by the search to find the most energetically favorable conformation of the protein, i.e., its
native state. Thus, understanding protein folding is critical to understanding what a protein does and how it works, and is considered a holy grail of
computational biology.
[12][13] Despite folding occurring within a
crowded cellular environment, it typically proceeds smoothly. However, due to a protein's chemical properties or other factors, proteins may
misfold, that is, fold down the wrong pathway and end up misshapen. Unless cellular mechanisms can destroy or refold misfolded proteins, they can subsequently
aggregate and cause a variety of debilitating diseases.
[14] Laboratory experiments studying these processes can be limited in scope and atomic detail, leading scientists to use physics-based computing models that, when complementing experiments, seek to provide a more complete picture of protein folding, misfolding, and aggregation.
[15][16]
Due to the complexity of proteins' conformation or
configuration space (the set of possible shapes a protein can take), and limits in computing power, all-atom molecular dynamics simulations have been severely limited in the timescales which they can study. While most proteins typically fold in the order of milliseconds,
[15][17] before 2010, simulations could only reach nanosecond to microsecond timescales.
[9] General-purpose
supercomputers have been used to simulate protein folding, but such systems are intrinsically costly and typically shared among many research groups. Further, because the computations in kinetic models occur serially, strong
scaling of traditional molecular simulations to these architectures is exceptionally difficult.
[18][19] Moreover, as protein folding is a
stochastic process and can statistically vary over time, it is challenging computationally to use long simulations for comprehensive views of the folding process.
[20][21]
Folding@home uses
Markov state models, like the one diagrammed here, to model the possible shapes and folding pathways a protein can take as it condenses from its initial randomly coiled state (left) into its native 3-D structure (right).
Protein folding does not occur in one step.
[14] Instead, proteins spend most of their folding time, nearly 96% in some cases,
[22] waiting in various intermediate
conformational states, each a local
thermodynamic free energy minimum in the protein's
energy landscape. Through a process known as
adaptive sampling, these conformations are used by Folding@home as starting points for a
set of simulation trajectories. As the simulations discover more conformations, the trajectories are restarted from them, and a
Markov state model (MSM) is gradually created from this cyclic process. MSMs are
discrete-time master equation models which describe a biomolecule's conformational and energy landscape as a set of distinct structures and the short transitions between them. The adaptive sampling Markov state model method significantly increases the efficiency of simulation as it avoids computation inside the local energy minimum itself, and is amenable to distributed computing (including on
GPUGRID) as it allows for the statistical aggregation of short, independent simulation trajectories.
[23] The amount of time it takes to construct a Markov state model is inversely proportional to the number of parallel simulations run, i.e., the number of processors available. In other words, it achieves linear
parallelization, leading to an approximately four
orders of magnitude reduction in overall serial calculation time. A completed MSM may contain tens of thousands of sample states from the protein's
phase space (all the conformations a protein can take on) and the transitions between them. The model illustrates folding events and pathways (i.e., routes) and researchers can later use kinetic clustering to view a coarse-grained representation of the otherwise highly detailed model. They can use these MSMs to reveal how proteins misfold and to quantitatively compare simulations with experiments.
[6][20][24]
Between 2000 and 2010, the length of the proteins Folding@home has studied have increased by a factor of four, while its timescales for protein folding simulations have increased by six orders of magnitude.
[25] In 2002, Folding@home used Markov state models to complete approximately a million
CPU days of simulations over the span of several months,
[11] and in 2011, MSMs parallelized another simulation that required an aggregate 10 million CPU hours of computing.
[26] In January 2010, Folding@home used MSMs to simulate the dynamics of the slow-folding 32-
residueNTL9 protein out to 1.52 milliseconds, a timescale consistent with experimental folding rate predictions but a thousand times longer than formerly achieved. The model consisted of many individual trajectories, each two orders of magnitude shorter, and provided an unprecedented level of detail into the protein's energy landscape.
[6][9][27] In 2010, Folding@home researcher Gregory Bowman was awarded the
Thomas Kuhn Paradigm Shift Award from the
American Chemical Society for the development of the
open-source MSMBuilder software and for attaining quantitative agreement between theory and experiment.
[28][29] For his work, Pande was awarded the 2012 Michael and Kate Bárány Award for Young Investigators for "developing field-defining and field-changing computational methods to produce leading theoretical models for protein and
RNAfolding",
[30] and the 2006 Irving Sigal Young Investigator Award for his simulation results which "have stimulated a re-examination of the meaning of both ensemble and single-molecule measurements, making Dr. Pande's efforts pioneering contributions to simulation methodology."
[31]
Examples of application in biomedical research[
edit]
Protein misfolding can result in a
variety of diseases including Alzheimer's disease,
cancer,
Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease,
cystic fibrosis, Huntington's disease,
sickle-cell anemia, and
type II diabetes.
[14][32][33] Cellular infection by viruses such as
HIV and
influenza also involve folding events on
cell membranes.
[34] Once protein misfolding is better understood, therapies can be developed that augment cells' natural ability to regulate protein folding. Such
therapies include the use of engineered molecules to alter the production of a given protein, help destroy a misfolded protein, or assist in the folding process.
[35] The combination of computational molecular modeling and experimental analysis has the possibility to fundamentally shape the future of molecular medicine and the
rational design of therapeutics,
[16] such as expediting and lowering the costs of
drug discovery.
[36] The goal of the first five years of Folding@home was to make advances in understanding folding, while the current goal is to understand misfolding and related disease, especially Alzheimer's.
[37]
The simulations run on Folding@home are used in conjunction with laboratory experiments,
[20] but researchers can use them to study how folding
in vitro differs from folding in native cellular environments. This is advantageous in studying aspects of folding, misfolding, and their relationships to disease that are difficult to observe experimentally. For example, in 2011, Folding@home simulated protein folding inside a
ribosomal exit tunnel, to help scientists better understand how natural confinement and crowding might influence the folding process.
[38][39]Furthermore, scientists typically employ chemical
denaturants to unfold proteins from their stable native state. It is not generally known how the denaturant affects the protein's refolding, and it is difficult to experimentally determine if these denatured states contain residual structures which may influence folding behavior. In 2010, Folding@home used GPUs to simulate the unfolded states of
Protein L, and predicted its collapse rate in strong agreement with experimental results.
[40]
The large data sets from the project are freely available for other researchers to use upon request and some can be accessed from the Folding@home website.
[41][42] The Pande lab has collaborated with other molecular dynamics systems such as the
Blue Gene supercomputer,
[43] and they share Folding@home's key software with other researchers, so that the algorithms which benefited Folding@home may aid other scientific areas.
[41] In 2011, they released the open-source Copernicus software, which is based on Folding@home's MSM and other parallelizing methods and aims to improve the efficiency and scaling of molecular simulations on large
computer clustersor
supercomputers.
[44][45] Summaries of all scientific findings from Folding@home are posted on the Folding@home website after publication.
[46]
Alzheimer's disease[
edit]



Alzheimer's disease is linked to the aggregation of amyloid beta protein fragments in the brain (right). Researchers have used Folding@home to simulate this aggregation process, to better understand the cause of the disease.
Alzheimer's disease is an incurable
neurodegenerative disease which most often affects the elderly and accounts for more than half of all cases of
dementia. Its exact cause remains unknown, but the disease is identified as a
protein misfolding disease. Alzheimer's is associated with toxic
aggregations of the
amyloid beta (Aβ)
peptide, caused by Aβ misfolding and clumping together with other Aβ peptides. These Aβ aggregates then grow into significantly larger
senile plaques, a pathological marker of Alzheimer's disease.
[47][48][49] Due to the heterogeneous nature of these aggregates, experimental methods such as
X-ray crystallography and
nuclear magnetic resonance(NMR) have had difficulty characterizing their structures. Moreover, atomic simulations of Aβ aggregation are highly demanding computationally due to their size and complexity.
[50][51]
Preventing Aβ aggregation is a promising method to developing therapeutic drugs for Alzheimer's disease, according to Drs. Naeem and Fazili in a
literature review article.
[52] In 2008, Folding@home simulated the dynamics of Aβ aggregation in atomic detail over timescales of the order of tens of seconds. Prior studies were only able to simulate about 10 microseconds. Folding@home was able to simulate Aβ folding for six orders of magnitude longer than formerly possible. Researchers used the results of this study to identify a
beta hairpin that was a major source of molecular interactions within the structure.
[53] The study helped prepare the Pande lab for future aggregation studies and for further research to find a small peptide which may stabilize the aggregation process.
[50]
In December 2008, Folding@home found several small drug candidates which appear to inhibit the toxicity of Aβ aggregates.
[54] In 2010, in close cooperation with the Center for Protein Folding Machinery, these drug leads began to be tested on
biological tissue.
[33] In 2011, Folding@home completed simulations of several
mutations of Aβ that appear to stabilize the aggregate formation, which could aid in the development of therapeutic drug therapies for the disease and greatly assist with experimental
nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies of Aβ
oligomers.
[51][55] Later that year, Folding@home began simulations of various Aβ fragments to determine how various natural enzymes affect the structure and folding of Aβ.
[56][57]
Huntington's disease[
edit]
Huntington's disease is a neurodegenerative
genetic disorder that is associated with protein misfolding and aggregation.
Excessive repeats of the
glutamine amino acid at the
N-terminus of the
huntingtin protein cause aggregation, and although the behavior of the repeats is not completely understood, it does lead to the cognitive decline associated with the disease.
[58] As with other aggregates, there is difficulty in experimentally determining its structure.
[59] Scientists are using Folding@home to study the structure of the huntingtin protein aggregate and to predict how it forms, assisting with
rational drug design methods to stop the aggregate formation.
[33] The N17 fragment of the huntingtin protein accelerates this aggregation, and while there have been several mechanisms proposed, its exact role in this process remains largely unknown.
[60] Folding@home has simulated this and other fragments to clarify their roles in the disease.
[61] Since 2008, its drug design methods for Alzheimer's disease have been applied to Huntington's.
[33]
Cancer[
edit]
More than half of all known cancers involve
mutations of
p53, a
tumor suppressor protein present in every cell which regulates the
cell cycle and signals for
cell death in the event of damage to
DNA. Specific mutations in p53 can disrupt these functions, allowing an abnormal cell to continue growing unchecked, resulting in the development of
tumors. Analysis of these mutations helps explain the root causes of p53-related cancers.
[62] In 2004, Folding@home was used to perform the first molecular dynamics study of the refolding of p53's
protein dimer in an
all-atom simulation of water. The simulation's results agreed with experimental observations and gave insights into the refolding of the dimer that were formerly unobtainable.
[63] This was the first
peer reviewed publication on cancer from a distributed computing project.
[64] The following year, Folding@home powered a new method to identify the amino acids crucial for the stability of a given protein, which was then used to study mutations of p53. The method was reasonably successful in identifying cancer-promoting mutations and determined the effects of specific mutations which could not otherwise be measured experimentally.
[65]
Folding@home is also used to study
protein chaperones,
[33] heat shock proteins which play essential roles in cell survival by assisting with the folding of other proteins in the
crowded and chemically stressful environment within a cell. Rapidly growing cancer cells rely on specific chaperones, and some chaperones play key roles in
chemotherapy resistance. Inhibitions to these specific chaperones are seen as potential modes of action for efficient chemotherapy drugs or for reducing the spread of cancer.
[66] Using Folding@home and working closely with the Center for Protein Folding Machinery, the Pande lab hopes to find a drug which inhibits those chaperones involved in cancerous cells.
[67] Researchers are also using Folding@home to study other molecules related to cancer, such as the enzyme
Src kinase, and some forms of the
engrailedhomeodomain: a large protein which may be involved in many diseases, including cancer.
[68][69] In 2011, Folding@home began simulations of the dynamics of the small
knottin protein EETI, which can identify
carcinomas in
imaging scans by binding to
surface receptors of cancer cells.
[70][71]
Interleukin 2 (IL-2) is a protein that helps
T cells of the
immune system attack pathogens and tumors. However, its use as a cancer treatment is restricted due to serious side effects such as
pulmonary edema. IL-2 binds to these pulmonary cells differently than it does to T cells, so IL-2 research involves understanding the differences between these binding mechanisms. In 2012, Folding@home assisted with the discovery of a mutant form of IL-2 which is three hundred times more effective in its immune system role but carries fewer side effects. In experiments, this altered form significantly outperformed natural IL-2 in impeding tumor growth.
Pharmaceutical companieshave expressed interest in the mutant molecule, and the
National Institutes of Health are testing it against a large variety of tumor models to try to accelerate its development as a therapeutic.
[72][73]
Osteogenesis imperfecta[
edit]
Osteogenesis imperfecta, known as brittle bone disease, is an incurable genetic bone disorder which can be lethal. Those with the disease are unable to make functional connective bone tissue. This is most commonly due to a mutation in
Type-I collagen,
[74] which fulfills a variety of structural roles and is the most abundant protein in
mammals.
[75] The mutation causes a deformation in
collagen's triple helix structure, which if not naturally destroyed, leads to abnormal and weakened bone tissue.
[76] In 2005, Folding@home tested a new
quantum mechanical method that improved upon prior simulation methods, and which may be useful for future computing studies of collagen.
[77] Although researchers have used Folding@home to study collagen folding and misfolding, the interest stands as a pilot project compared to
Alzheimer's and Huntington's research.
[33]
Viruses[
edit]
Folding@home is assisting in research towards preventing some
viruses, such as
influenza and
HIV, from recognizing and entering
biological cells.
[33] In 2011, Folding@home began simulations of the dynamics of the enzyme
RNase H, a key component of HIV, to try to design drugs to deactivate it.
[78] Folding@home has also been used to study
membrane fusion, an essential event for
viral infection and a wide range of biological functions. This fusion involves
conformational changes of viral fusion proteins and
protein docking,
[34] but the exact molecular mechanisms behind fusion remain largely unknown.
[79] Fusion events may consist of over a half million atoms interacting for hundreds of microseconds. This complexity limits typical computer simulations to about ten thousand atoms over tens of nanoseconds: a difference of several orders of magnitude.
[53] The development of models to predict the mechanisms of membrane fusion will assist in the scientific understanding of how to target the process with antiviral drugs.
[80] In 2006, scientists applied Markov state models and the Folding@home network to discover two pathways for fusion and gain other mechanistic insights.
[53]
Following detailed simulations from Folding@home of small cells known as
vesicles, in 2007, the Pande lab introduced a new computing method to measure the
topology of its structural changes during fusion.
[81] In 2009, researchers used Folding@home to study mutations of
influenza hemagglutinin, a protein that attaches a virus to its
host cell and assists with viral entry. Mutations to hemagglutinin affect
how well the protein binds to a host's
cell surface receptor molecules, which determines how
infective the virus strain is to the host organism. Knowledge of the effects of hemagglutinin mutations assists in the development of
antiviral drugs.
[82][83] As of 2012, Folding@home continues to simulate the folding and interactions of hemagglutinin, complementing experimental studies at the
University of Virginia.
[33][84]
In March 2020, Folding@home launched a program to assist researchers around the world who are working on finding a cure and learning more about the
coronavirus pandemic. The initial wave of projects simulate potentially druggable protein targets from SARS-CoV-2 virus, and the related SARS-CoV virus, about which there is significantly more data available.
[85][86][87]
Drug design[
edit]
Drugs function by
binding to
specific locations on target molecules and causing some desired change, such as disabling a target or causing a
conformational change. Ideally, a drug should act very specifically, and bind only to its target without interfering with other biological functions. However, it is difficult to precisely determine where and
how tightly two molecules will bind. Due to limits in computing power, current
in silico methods usually must trade speed for
accuracy; e.g., use rapid
protein docking methods instead of computationally costly
free energy calculations. Folding@home's computing performance allows researchers to use both methods, and evaluate their efficiency and reliability.
[37][88][89] Computer-assisted drug design has the potential to expedite and lower the costs of drug discovery.
[36] In 2010, Folding@home used MSMs and free energy calculations to predict the native state of the
villin protein to within 1.8
angstrom (Å)
root mean square deviation (RMSD) from the
crystalline structure experimentally determined through
X-ray crystallography. This accuracy has implications to future
protein structure prediction methods, including for
intrinsically unstructured proteins.
[53] Scientists have used Folding@home to research
drug resistance by studying
vancomycin, an antibiotic
drug of last resort, and
beta-lactamase, a protein that can break down antibiotics like
penicillin.
[90][91]
Chemical activity occurs along a protein's
active site. Traditional drug design methods involve tightly binding to this site and blocking its activity, under the assumption that the target protein exists in one rigid structure. However, this approach works for approximately only 15% of all proteins. Proteins contain
allosteric sites which, when bound to by small molecules, can alter a protein's conformation and ultimately affect the protein's activity. These sites are attractive drug targets, but locating them is very
computationally costly. In 2012, Folding@home and MSMs were used to identify allosteric sites in three medically relevant proteins: beta-lactamase,
interleukin-2, and
RNase H.
[91][92]
Approximately half of all known
antibiotics interfere with the workings of a bacteria's
ribosome, a large and complex biochemical machine that performs
protein biosynthesis by
translatingmessenger RNA into proteins.
Macrolide antibiotics clog the ribosome's exit tunnel, preventing synthesis of essential bacterial proteins. In 2007, the Pande lab received a
grant to study and design new antibiotics.
[33] In 2008, they used Folding@home to study the interior of this tunnel and how specific molecules may affect it.
[93] The full structure of the ribosome was determined only as of 2011, and Folding@home has also simulated
ribosomal proteins, as many of their functions remain largely unknown.
[94]
Potential applications in biomedical research[
edit]
There are many more
protein misfolding promoted diseases that can be benefited from Folding@home to either discern the misfolded protein structure or the misfolding kinetics, and assist in drug design in the future. The often fatal
prion diseases is among the most significant.
Prion diseases[
edit]

This section possibly contains
synthesis of material which does not
verifiably mention or
relate to the main topic.Relevant discussion may be found on the
talk page. (March 2020)(
Learn how and when to remove this template message)
Prion (PrP) is a
transmembrane cellular protein found widely in
eukaryotic cells. In mammals, it is more abundant in the
central nervous system. Although its function is unknown, its high conservation among species indicates an important role in the cellular function. The conformational change from the normal prion protein (PrPc, stands for cellular) to the disease causing
isoformPrPSc (stands for prototypical prion disease–
scrapie) causes a host of diseases collectly known as
transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs), including
Bovine spongiform encephalopathy(BSE) in bovine,
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) and
fatal insomnia in human,
chronic wasting disease (CWD) in the deer family. The conformational change is widely accepted as the result of
protein misfolding. What distinguishes TSEs from other protein misfolding diseases is its transmissible nature. The ‘seeding’ of the infectious PrPSc, either arising spontaneously, hereditary or acquired via exposure to contaminated tissues,
[95] can cause a chain reaction of transforming normal PrPc into
fibrils aggregates or
amyloid like plaques consist of PrPSc.
[96]
The molecular structure of PrPSc has not been fully characterized due to its aggregated nature. Neither is known much about the mechanism of the protein misfolding nor its
kinetics. Using the known structure of PrPc and the results of the in vitro and in vivo studies described below, Folding@home could be valuable in elucidating how PrPSc is formed and how the infectious protein arrange themselves to form fibrils and amyloid like plaques, bypassing the requirement to purify PrPSc or dissolve the aggregates.
The PrPc has been
enzymatically dissociated from the membrane and purified, its structure studied using structure characterization techniques such as
NMR spectroscopy and
X-ray crystallography.
Post-translational PrPc has 231
amino acids (aa) in murine. The molecule consists of a long and unstructured
amino terminal region spanning up to aa residue 121 and a structured
carboxy terminal domain.
[96] This globular domain harbours two short sheet-forming anti-parallel
β-strands(aa 128 to 130 and aa 160 to 162 in murine PrPc) and three
α-helices (helix I: aa 143 to 153; helix II: aa 171 to 192; helix III: aa 199 to 226 in murine PrPc),
[97] Helices II and III are anti-parallel orientated and connected by a short loop. Their structural stability is supported by a
disulfide bridge, which is parallel to both sheet-forming β-strands. These α-helices and the β-sheet form the rigid core of the globular domain of PrPc.
[98]
The disease causing PrPSc is
proteinase K resistant and insoluble. Attempts to purify it from the brains of infected animals invariably yield heterogeneous mixtures and aggregated states that are not amenable to characterization by NMR spectroscopy or X-ray crystallography. However, it is a general consensus that PrPSc contains a high percentage of tightly stacked β-sheets than the normal PrPc that renders the protein insoluble and resistant to proteinase. Using techniques of
cryoelectron microscopy and structural modeling based on similar common protein structures, it has been discovered that PrPSc contains ß-sheets in the region of aa 81-95 to aa 171, while the carboxy terminal structure is supposedly preserved, retaining the disulfide-linked α-helical conformation in the normal PrPc. These ß-sheets form a parallel left-handed beta-helix.
[96] Three PrPSc molecules are believed to form a primary unit and therefore build the basis for the so-called scrapie-associated fibrils.
[99] The catalytic activity depends on the size of the particle. PrPSc particles which consist of only 14-28 PrPc molecules exhibit the highest rate of infectivity and conversion.
[100]
Despite the difficulty to purify and characterize PrPSc, from the known molecular structure of PrPc and using
transgenic mice and N-terminal deletion,
[101] the potential ‘hot spots’ of protein misfolding leading to the pathogenic PrPSc could be deduced and Folding@home could be of great value in confirming these. Studies found that both the
primary and
secondary structure of the prion protein can be of significance of the conversion.
There are more than twenty
mutations of the prion protein gene (
PRNP) that are known to be associated with or that are directly linked to the hereditary form of human TSEs [56], indicating single amino acids at certain position, likely within the carboxy domain,
[97] of the PrPc can affect the susceptibility to TSEs.
The post-translational amino terminal region of PrPc consists of residues 23-120 which make up nearly half of the amino sequence of full-length matured PrPc. There are two sections in the amino terminal region that may influence conversion. First, residues 52-90 contains an octapeptide repeat (5 times) region that likely influences the initial binding (via the octapeptide repeats) and also the actual conversion via the second section of aa 108–124.
[102] The highly
hydrophobic AGAAAAGA is located between aa residue 113 and 120 and is described as putative aggregation site,
[103]although this sequence requires its flanking parts to form fibrillar aggregates.
[104]
In the carboxy globular domain,
[98] among the three helices, study show that helix II has a significant higher propensity to β-strand conformation.
[105] Due to the high conformational flexvoribility seen between residues 114-125 (part of the unstructured N-terminus chain) and the high β-strand propensity of helix II, only moderate changes in the environmental conditions or interactions might be sufficient to induce misfolding of PrPc and subsequent fibril formation.
[96]
Other studies of NMR structures of PrPc showed that these residues (~108–189) contain most of the folded domain including both β-strands, the first two α-helices, and the loop/turn regions connecting them, but not the helix III.
[101] Small changes within the loop/turn structures of PrPc itself could be important in the conversion as well.
[106] In another study, Riek et al. showed that the two small regions of β-strand upstream of the loop regions act as a nucleation site for the conformational conversion of the loop/turn and α-helical structures in PrPc to β-sheet.
[97]
The energy threshold for the conversion are not necessarily high. The folding stability, i.e. the
free energy of a globular protein in its environment is in the range of one or two
hydrogen bonds thus allows the transition to an isoform without the requirement of high transition energy.
[96]
From the respective of the interactions among the PrPc molecules, hydrophobic interactions play a crucial role in the formation of β-sheets, a hallmark of PrPSc, as the sheets bring fragments of
polypeptide chains into close proximity.
[107] Indeed, Kutznetsov and Rackovsky
[108] showed that disease-promoting mutations in the human PrPc had a statistically significant tendency towards increasing local hydrophobicity.
In vitro experiments showed the kinetics of misfolding has an initial lag phase followed by a rapid growth phase of fibril formation.
[109] It is likely that PrPc goes through some intermediate states, such as at least partially unfolded or degraded, before finally ending up as part of an amyloid fibril.
[96]
Patterns of participation[
edit]
Like other
distributed computing projects, Folding@home is an online
citizen science project. In these projects non-specialists contribute computer processing power or help to analyse data produced by professional scientists. Participants in these projects play an invaluable role in facilitating research for little or no obvious reward.
Research has been carried out into the motivations of citizen scientists and most of these studies have found that participants are motivated to take part because of altruistic reasons, that is, they want to help scientists and make a contribution to the advancement of their research.
[110][111][112][113] Many participants in citizen science have an underlying interest in the topic of the research and gravitate towards projects that are in disciplines of interest to them. Folding@home is no different in that respect.
[114] Research carried out recently on over 400 active participants revealed that they wanted to help make a contribution to research and that many had friends or relatives affected by the diseases that the Folding@home scientists investigate.
Folding@home attracts participants who are computer hardware enthusiasts (sometimes called ‘overclockers’). These groups bring considerable expertise to the project and are able to build computers with advanced processing power.
[115] Other distributed computing projects attract these types of participants and projects are often used to benchmark the performance of modified computers, and this aspect of the hobby is accommodated through the competitive nature of the project. Individuals and teams can compete to see who can process the most computer processing units (CPUs).
This latest research on Folding@home involving interview and ethnographic observation of online groups showed that teams of hardware enthusiasts can sometimes work together, sharing best practice with regard to maximising processing output. Such teams can become
communities of practice, with a shared language and online culture. This pattern of participation has been observed in other distributed computing projects.
[116][117]
Another key observation of Folding@home participants is that many are male.
[114] This has also been observed in other distributed projects. Furthermore, many participants work in computer and technology-based jobs and careers.
[114][118][119]
Not all Folding@home participants are hardware enthusiasts. Many participants run the project software on unmodified machines and do take part competitively. Over 100,000 participants are involved in Folding@home. However, it is difficult to ascertain what proportion of participants are hardware enthusiasts. Although, according to the project managers, the contribution of the enthusiast community is substantially larger in terms of processing power.
[120]
Performance[
edit]

Computing power of Folding@home and the fastest supercomputer from April 2004 to October 2012. Between June 2007 and June 2011, Folding@home (red) exceeded the performance of
Top500's fastest supercomputer (black). However it was eclipsed by
K computer in November 2011 and
Blue Gene/Q in June 2012.
Supercomputer FLOPS performance is assessed by running the legacy
LINPACK benchmark. This short-term testing has difficulty in accurately reflecting sustained performance on real-world tasks because LINPACK more efficiently maps to supercomputer hardware. Computing systems vary in architecture and design, so direct comparison is difficult. Despite this, FLOPS remain the primary speed metric used in supercomputing.
[121][
need quotation to verify] In contrast, Folding@home determines its FLOPS using
wall-clock time by measuring how much time its work units take to complete.
[122]
On September 16, 2007, due in large part to the participation of PlayStation 3 consoles, the Folding@home project officially attained a sustained performance level higher than one native
petaFLOPS, becoming the first computing system of any kind to do so.
[123][124] Top500's fastest supercomputer at the time was
BlueGene/L, at 0.280 petaFLOPS.
[125] The following year, on May 7, 2008, the project attained a sustained performance level higher than two native petaFLOPS,
[126] followed by the three and four native petaFLOPS milestones on August 2008
[127][128] and September 28, 2008 respectively.
[129] On February 18, 2009, Folding@home achieved five native petaFLOPS,
[130][131] and was the first computing project to meet these five levels.
[132][133] In comparison, November 2008's fastest supercomputer was
IBM's
Roadrunner at 1.105 petaFLOPS.
[134] On November 10, 2011, Folding@home's performance exceeded six native petaFLOPS with the equivalent of nearly eight x86 petaFLOPS.
[124][135] In mid-May 2013, Folding@home attained over seven native petaFLOPS, with the equivalent of 14.87 x86 petaFLOPS. It then reached eight native petaFLOPS on June 21, followed by nine on September 9 of that year, with 17.9 x86 petaFLOPS.
[136] On May 11, 2016 Folding@home announced that it was moving towards reaching the 100 x86 petaFLOPS mark.
[137]
Further use grew from increased awareness and participation in the project from the coronavirus pandemic in 2020. On March 20, 2020 Folding@home announced via Twitter that it was running with over 470 native petaFLOPS
[138], the equivalent of 958 x86 petaFLOPS.
[139] By March 25 it reached 768 petaFLOPS, or 1.5 x86 exaFLOPS, making it the first
exaFLOP computing system.
[140]
Points[
edit]
Similarly to other distributed computing projects, Folding@home quantitatively assesses user computing contributions to the project through a credit system.
[141] All units from a given protein project have uniform base credit, which is determined by benchmarking one or more work units from that project on an official reference machine before the project is released.
[141] Each user receives these base points for completing every work unit, though through the use of a passkey they can receive added bonus points for reliably and rapidly completing units which are more demanding computationally or have a greater scientific priority.
[142][143] Users may also receive credit for their work by clients on multiple machines.
[144] This point system attempts to align awarded credit with the value of the scientific results.
[141]
Users can register their contributions under a team, which combine the points of all their members. A user can start their own team, or they can join an existing team. In some cases, a team may have their own community-driven sources of help or recruitment such as an
Internet forum.
[145] The points can foster friendly competition between individuals and teams to compute the most for the project, which can benefit the folding community and accelerate scientific research.
[141][146][147]Individual and team statistics are posted on the Folding@home website.
[141]
If a user does not form a new team, or does not join an existing team, that user automatically becomes part of a "Default" team. This "Default" team has a team number of "0". Statistics are accumulated for this "Default" team as well as for specially named teams.
Software[
edit]
Folding@home software at the user's end involves three primary components: work units, cores, and a client.
Work units[
edit]
A work unit is the protein data that the client is asked to process. Work units are a fraction of the simulation between the states in a
Markov model. After the work unit has been downloaded and completely processed by a volunteer's computer, it is returned to Folding@home servers, which then award the volunteer the credit points. This cycle repeats automatically.
[146] All work units have associated deadlines, and if this deadline is exceeded, the user may not get credit and the unit will be automatically reissued to another participant. As protein folding occurs serially, and many work units are generated from their predecessors, this allows the overall simulation process to proceed normally if a work unit is not returned after a reasonable period of time. Due to these deadlines, the minimum system requirement for Folding@home is a Pentium 3 450 MHz CPU with
Streaming SIMD Extensions (SSE).
[144] However, work units for high-performance clients have a much shorter deadline than those for the uniprocessor client, as a major part of the scientific benefit is dependent on rapidly completing simulations.
[148]
Before public release, work units go through several
quality assurance steps to keep problematic ones from becoming fully available. These testing stages include internal, beta, and advanced, before a final full release across Folding@home.
[149] Folding@home's work units are normally processed only once, except in the rare event that errors occur during processing. If this occurs for three different users, the unit is automatically pulled from distribution.
[150][151] The Folding@home support forum can be used to differentiate between issues arising from problematic hardware and bad work units.
[152]
Cores[
edit]
Main article:
List of Folding@home cores
Specialized molecular dynamics programs, referred to as "FahCores" and often abbreviated "cores", perform the calculations on the work unit as a
background process. A large majority of Folding@home's cores are based on
GROMACS,
[146] one of the fastest and most popular molecular dynamics software packages, which largely consists of manually optimized
assembly language code and hardware optimizations.
[153][154] Although GROMACS is
open-source softwareand there is a cooperative effort between the Pande lab and GROMACS developers, Folding@home uses a
closed-source license to help ensure data validity.
[155] Less active cores include ProtoMol and SHARPEN. Folding@home has used
AMBER,
CPMD,
Desmond, and
TINKER, but these have since been retired and are no longer in active service.
[3][156][157] Some of these cores perform
explicit solvation calculations in which the surrounding
solvent (usually water) is modeled atom-by-atom; while others perform
implicit solvation methods, where the solvent is treated as a mathematical continuum.
[158][159] The core is separate from the client to enable the scientific methods to be updated automatically without requiring a client update. The cores periodically create calculation
checkpoints so that if they are interrupted they can resume work from that point upon startup.
[146]
Client[
edit]

Folding@Home running on Fedora 25
A Folding@home participant installs a
client program on their
personal computer. The user interacts with the client, which manages the other software components in the background. Through the client, the user may pause the folding process, open an event log, check the work progress, or view personal statistics.
[160] The computer clients run continuously in the
background at a very low priority, using idle processing power so that normal computer use is unaffected.
[144] The maximum CPU use can be adjusted via client settings.
[160][161] The client connects to a Folding@home
server and retrieves a work unit and may also download the appropriate core for the client's settings, operating system, and the underlying hardware architecture. After processing, the work unit is returned to the Folding@home servers. Computer clients are tailored to
uniprocessor and
multi-core processorsystems, and
graphics processing units. The diversity and power of each
hardware architectureprovides Folding@home with the ability to efficiently complete many types of simulations in a timely manner (in a few weeks or months rather than years), which is of significant scientific value. Together, these clients allow researchers to study biomedical questions formerly considered impractical to tackle computationally.
[37][146][148]
Professional software developers are responsible for most of Folding@home's code, both for the client and server-side. The development team includes programmers from Nvidia, ATI, Sony, and Cauldron Development.
[162] Clients can be downloaded only from the official Folding@home website or its commercial partners, and will only interact with Folding@home computer files. They will upload and download data with Folding@home's data servers (over
port 8080, with 80 as an alternate), and the communication is verified using 2048-bit
digital signatures.
[144][163] While the client's
graphical user interface (GUI) is open-source,
[164] the client is
proprietary software citing security and scientific integrity as the reasons.
[165][166][167]
However, this rationale of using proprietary software is disputed since while the license could be enforceable in the legal domain retrospectively, it doesn't practically prevent the modification (also known as
patching) of the executable
binary files. Likewise,
binary-only distribution does not prevent the malicious modification of executable binary-code, either through a
man-in-the-middle attack while being downloaded via the internet,
[168] or by the redistribution of binaries by a third-party that have been previously modified either in their binary state (i.e.
patched),
[169] or by decompiling
[170] and recompiling them after modification.
[171][172] These modifications are possible unless the binary files – and the transport channel – are
signed and the recipient person/system is able to verify the digital signature, in which case unwarranted modifications should be detectable, but not always.
[173] Either way, since in the case of Folding@home the input data and output result processed by the client-software are both digitally signed,
[144][163] the integrity of work can be verified independently from the integrity of the client software itself.
Folding@home uses the
Cosm software libraries for networking.
[146][162] Folding@home was launched on October 1, 2000, and was the first distributed computing project aimed at bio-molecular systems.
[174] Its first client was a
screensaver, which would run while the computer was not otherwise in use.
[175][176] In 2004, the Pande lab collaborated with
David P. Anderson to test a supplemental client on the open-source
BOINC framework. This client was released to closed beta in April 2005;
[177] however, the method became unworkable and was shelved in June 2006.
[178]
Graphics processing units[
edit]
The specialized hardware of
graphics processing units (GPU) is designed to accelerate rendering of 3-D graphics applications such as video games and can significantly outperform CPUs for some types of calculations. GPUs are one of the most powerful and rapidly growing computing platforms, and many scientists and researchers are pursuing
general-purpose computing on graphics processing units (GPGPU). However, GPU hardware is difficult to use for non-graphics tasks and usually requires significant algorithm restructuring and an advanced understanding of the underlying architecture.
[179] Such customization is challenging, more so to researchers with limited software development resources. Folding@home uses the
open-source OpenMM library, which uses a
bridge design pattern with two
application programming interface (API) levels to interface molecular simulation software to an underlying hardware architecture. With the addition of hardware optimizations, OpenMM-based GPU simulations need no significant modification but achieve performance nearly equal to hand-tuned GPU code, and greatly outperform CPU implementations.
[158][180]
Before 2010, the computing reliability of GPGPU consumer-grade hardware was largely unknown, and circumstantial evidence related to the lack of built-in
error detection and correction in GPU memory raised reliability concerns. In the first large-scale test of GPU scientific accuracy, a 2010 study of over 20,000 hosts on the Folding@home network detected
soft errors in the memory subsystems of two-thirds of the tested GPUs. These errors strongly correlated to board architecture, though the study concluded that reliable GPU computing was very feasible as long as attention is paid to the hardware traits, such as software-side error detection.
[181]
The first generation of Folding@home's GPU client (GPU1) was released to the public on October 2, 2006,
[178] delivering a 20–30 times speedup for some calculations over its CPU-based
GROMACS counterparts.
[182] It was the first time GPUs had been used for either distributed computing or major molecular dynamics calculations.
[183][184] GPU1 gave researchers significant knowledge and experience with the development of
GPGPU software, but in response to scientific inaccuracies with
DirectX, on April 10, 2008 it was succeeded by GPU2, the second generation of the client.
[182][185] Following the introduction of GPU2, GPU1 was officially retired on June 6.
[182]Compared to GPU1, GPU2 was more scientifically reliable and productive, ran on
ATI and
CUDA-enabled
Nvidia GPUs, and supported more advanced algorithms, larger proteins, and real-time visualization of the protein simulation.
[186][187] Following this, the third generation of Folding@home's GPU client (GPU3) was released on May 25, 2010. While
backward compatiblewith GPU2, GPU3 was more stable, efficient, and flexibile in its scientific abilities,
[188] and used OpenMM on top of an
OpenCL framework.
[188][189] Although these GPU3 clients did not natively support the operating systems
Linux and
macOS, Linux users with Nvidia graphics cards were able to run them through the
Wine software application.
[190][191] GPUs remain Folding@home's most powerful platform in
FLOPS. As of November 2012, GPU clients account for 87% of the entire project's x86 FLOPS throughput.
[192]
Native support for Nvidia and AMD graphics cards under Linux was introduced with FahCore 17, which uses OpenCL rather than CUDA.
[193]
PlayStation 3[
edit]
Further information:
Life with PlayStation

The PlayStation 3's Life With PlayStation client displays a 3-D animation of the protein being folded
From March 2007 until November 2012, Folding@home took advantage of the computing power of
PlayStation 3s. At the time of its inception, its main
streaming Cell processor delivered a 20 times speed increase over PCs for some calculations, processing power which could not be found on other systems such as the
Xbox 360.
[37][194]The PS3's high speed and efficiency introduced other opportunities for worthwhile optimizations according to
Amdahl's law, and significantly changed the tradeoff between computing efficiency and overall accuracy, allowing the use of more complex molecular models at little added computing cost.
[195] This allowed Folding@home to run biomedical calculations that would have been otherwise infeasible computationally.
[196]
The PS3 client was developed in a collaborative effort between
Sony and the Pande lab and was first released as a standalone client on March 23, 2007.
[37][197] Its release made Folding@home the first distributed computing project to use PS3s.
[198] On September 18 of the following year, the PS3 client became a channel of
Life with PlayStation on its launch.
[199][200] In the types of calculations it can perform, at the time of its introduction, the client fit in between a CPU's flexibility and a GPU's speed.
[146] However, unlike clients running on
personal computers, users were unable to perform other activities on their PS3 while running Folding@home.
[196] The PS3's uniform console environment made
technical support easier and made Folding@home more
user friendly.
[37] The PS3 also had the ability to stream data quickly to its GPU, which was used for real-time atomic-level visualizing of the current protein dynamics.
[195]
On November 6, 2012, Sony ended support for the Folding@home PS3 client and other services available under Life with PlayStation. Over its lifetime of five years and seven months, more than 15 million users contributed over 100 million hours of computing to Folding@home, greatly assisting the project with disease research. Following discussions with the Pande lab, Sony decided to terminate the application. Pande considered the PlayStation 3 client a "game changer" for the project.
[201][202][203]
Multi-core processing client[
edit]
Folding@home can use the
parallel computing abilities of modern multi-core processors. The ability to use several CPU cores simultaneously allows completing the full simulation far faster. Working together, these CPU cores complete single work units proportionately faster than the standard uniprocessor client. This method is scientifically valuable because it enables much longer simulation trajectories to be performed in the same amount of time, and reduces the traditional difficulties of scaling a large simulation to many separate processors.
[204] A 2007 publication in the
Journal of Molecular Biology relied on multi-core processing to simulate the folding of part of the
villin protein approximately 10 times longer than was possible with a single-processor client, in agreement with experimental folding rates.
[205]
In November 2006, first-generation
symmetric multiprocessing (SMP) clients were publicly released for open beta testing, referred to as SMP1.
[178] These clients used
Message Passing Interface(MPI) communication protocols for parallel processing, as at that time the GROMACS cores were
not designed to be used with multiple threads.
[148] This was the first time a distributed computing project had used MPI.
[206] Although the clients performed well in
Unix-based operating systems such as Linux and macOS, they were troublesome under
Windows.
[204][206] On January 24, 2010, SMP2, the second generation of the SMP clients and the successor to SMP1, was released as an open beta and replaced the complex MPI with a more reliable
thread-based implementation.
[143][162]
SMP2 supports a trial of a special category of bigadv work units, designed to simulate proteins that are unusually large and computationally intensive and have a great scientific priority. These units originally required a minimum of eight CPU cores,
[207] which was raised to sixteen later, on February 7, 2012.
[208] Along with these added hardware requirements over standard SMP2 work units, they require more system resources such as
random-access memory (RAM) and
Internet bandwidth. In return, users who run these are rewarded with a 20% increase over SMP2's bonus point system.
[209] The bigadv category allows Folding@home to run especially demanding simulations for long times that had formerly required use of supercomputing
clusters and could not be performed anywhere else on Folding@home.
[207] Many users with hardware able to run bigadv units have later had their hardware setup deemed ineligible for bigadv work units when CPU core minimums were increased, leaving them only able to run the normal SMP work units. This frustrated many users who invested significant amounts of money into the program only to have their hardware be obsolete for bigadv purposes shortly after. As a result, Pande announced in January 2014 that the bigadv program would end on January 31, 2015.
[210]
V7[
edit]

A sample image of the V7 client in Novice mode running under
Windows 7. In addition to a variety of controls and user details, V7 presents work unit information, such as its state, calculation progress, ETA, credit points, identification numbers, and description.
The V7 client is the seventh and latest generation of the Folding@home client software, and is a full rewrite and unification of the prior clients for
Windows,
macOS, and
Linux operating systems.
[211][212] It was released on March 22, 2012.
[213] Like its predecessors, V7 can run Folding@home in the background at a very low
priority, allowing other applications to use CPU resources as they need. It is designed to make the installation, start-up, and operation more user-friendly for novices, and offer greater scientific flexibility to researchers than prior clients.
[214] V7 uses
Trac for
managing its bug tickets so that users can see its development process and provide feedback.
[212]
V7 consists of four integrated elements. The user typically interacts with V7's open-source
GUI, named FAHControl.
[164][215] This has Novice, Advanced, and Expert user interface modes, and has the ability to monitor, configure, and control many remote folding clients from one computer. FAHControl directs FAHClient, a
back-end application that in turn manages each FAHSlot (or slot). Each slot acts as replacement for the formerly distinct Folding@home v6 uniprocessor, SMP, or GPU computer clients, as it can download, process, and upload work units independently. The FAHViewer function, modeled after the PS3's viewer, displays a real-time 3-D rendering, if available, of the protein currently being processed.
[211][212]
Google Chrome[
edit]
In 2014, a client for the
Google Chrome and
Chromium web browsers was released, allowing users to run Folding@home in their web browser. The client used
Google's
Native Client (NaCl) feature on Chromium-based web browsers to run the Folding@home code at near-native speed in a
sandbox on the user's machine.
[216] Due to the phasing out of NaCL and changes at Folding@home, the web client was permanently shut down in June 2019.
[217]
Android[
edit]
In July 2015, a client for
Android mobile phones was released on
Google Play for devices running
Android 4.4 KitKat or newer.
[218][219]
On the 16th of February 2018 the Android client, which was offered in cooperation with
Sony, was removed from the Google Play. Plans were announced to offer an open source alternative in the future.
[220]
Comparison to other molecular simulators[
edit]
Rosetta@home is a distributed computing project aimed at protein structure prediction and is one of the most accurate
tertiary structure predictors.
[221][222] The conformational states from Rosetta's software can be used to initialize a Markov state model as starting points for Folding@home simulations.
[23] Conversely, structure prediction algorithms can be improved from thermodynamic and kinetic models and the sampling aspects of protein folding simulations.
[223] As Rosetta only tries to predict the final folded state, and not how folding proceeds, Rosetta@home and Folding@home are complementary and address very different molecular questions.
[23][224]
Anton is a special-purpose supercomputer built for molecular dynamics simulations. In October 2011, Anton and Folding@home were the two most powerful molecular dynamics systems.
[225]Anton is unique in its ability to produce single ultra-long computationally costly molecular trajectories,
[226] such as one in 2010 which reached the millisecond range.
[227][228] These long trajectories may be especially helpful for some types of biochemical problems.
[229][230] However, Anton does not use Markov state models (MSM) for analysis. In 2011, the Pande lab constructed a MSM from two 100-
µs Anton simulations and found alternative folding pathways that were not visible through Anton's traditional analysis. They concluded that there was little difference between MSMs constructed from a limited number of long trajectories or one assembled from many shorter trajectories.
[226] In June 2011 Folding@home added sampling of an Anton simulation in an effort to better determine how its methods compare to Anton's.
[231][232] However, unlike Folding@home's shorter trajectories, which are more amenable to distributed computing and other parallelizing methods, longer trajectories do not require adaptive sampling to sufficiently sample the protein's
phase space. Due to this, it is possible that a combination of Anton's and Folding@home's simulation methods would provide a more thorough sampling of this space.
[226]
See also[
edit]
 Biology portal
Biology portal
 Medicine portal
BOINC
Foldit
List of distributed computing projects
Comparison of software for molecular mechanics modeling
Molecular modeling on GPUs
SETI@home
Storage@home
Molecule editor
World Community Grid
Medicine portal
BOINC
Foldit
List of distributed computing projects
Comparison of software for molecular mechanics modeling
Molecular modeling on GPUs
SETI@home
Storage@home
Molecule editor
World Community Grid
References[
edit]
^ foldingathome.org (September 27, 2016).
"About Folding@home Partners".
^
Bowman, Greg (April 17, 2020).
"New Folding@home software with the option to prioritize COVID-19 projects". Folding@home. Retrieved April 18, 2020.
"Alternative Downloads". Folding@home. Retrieved April 18, 2020.
^
Jump up to: a b Pande lab (August 2, 2012).
"Folding@home Open Source FAQ". Folding@home. foldingathome.org. Archived from
the original (FAQ) on March 3, 2020. Retrieved July 8, 2013.
^ Folding@home n.d.e: "Folding@home (FAH or F@h) is a distributed computing project for simulating protein dynamics, including the process of protein folding and the movements of proteins implicated in a variety of diseases. It brings together citizen scientists who volunteer to run simulations of protein dynamics on their personal computers. Insights from this data are helping scientists to better understand biology, and providing new opportunities for developing therapeutics."
^ Julia Evangelou Strait (February 26, 2019).
"Computational biology project aims to better understand protein folding". Retrieved March 8, 2020.
^
Jump up to: a b c V. S. Pande; K. Beauchamp; G. R. Bowman (2010).
"Everything you wanted to know about Markov State Models but were afraid to ask". Methods. 52 (1): 99–105.
doi:
10.1016/j.ymeth.2010.06.002.
PMC 2933958.
PMID 20570730.
^ Pande lab.
"Client Statistics by OS". Archive.is. Retrieved April 12, 2020.
^ "Papers & Results". Folding@home.org. Retrieved March 13, 2020.
^
Jump up to: a b c Vincent A. Voelz; Gregory R. Bowman; Kyle Beauchamp; Vijay S. Pande (2010).
"Molecular simulation of ab initio protein folding for a millisecond folder NTL9(1–39)". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 132 (5): 1526–1528.
doi:
10.1021/ja9090353.
PMC 2835335.
PMID 20070076.
^ Gregory R. Bowman; Vijay S. Pande (2010).
"Protein folded states are kinetic hubs". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 107 (24): 10890–5.
Bibcode:
2010PNAS..10710890B.
doi:
10.1073/pnas.1003962107.
PMC 2890711.
PMID 20534497.
^
Jump up to: a b Christopher D. Snow; Houbi Nguyen; Vijay S. Pande; Martin Gruebele (2002).
"Absolute comparison of simulated and experimental protein-folding dynamics" (PDF). Nature. 420 (6911): 102–106.
Bibcode:
2002Natur.420..102S.
doi:
10.1038/nature01160.
PMID 12422224. Archived from
the original (PDF) on March 24, 2012.
^ Fabrizio Marinelli, Fabio Pietrucci, Alessandro Laio, Stefano Piana (2009). Pande, Vijay S. (ed.).
"A Kinetic Model of Trp-Cage Folding from Multiple Biased Molecular Dynamics Simulations". PLOS Computational Biology. 5 (8): e1000452.
Bibcode:
2009PLSCB...5E0452M.
doi:
10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000452.
PMC 2711228.
PMID 19662155.
^ "So Much More to Know". Science. 309 (5731): 78–102. 2005.
doi:
10.1126/science.309.5731.78b.
PMID 15994524.
^
Jump up to: a b c Heath Ecroyd; John A. Carver (2008).
"Unraveling the mysteries of protein folding and misfolding". IUBMB Life (review). 60 (12): 769–774.
doi:
10.1002/iub.117.
PMID 18767168.
^
Jump up to: a b Yiwen Chen; Feng Ding; Huifen Nie; Adrian W. Serohijos; Shantanu Sharma; Kyle C. Wilcox; Shuangye Yin; Nikolay V. Dokholyan (2008).
"Protein folding: Then and now". Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 469 (1): 4–19.
doi:
10.1016/j.abb.2007.05.014.
PMC 2173875.
PMID 17585870.
^
Jump up to: a b Leila M Luheshi; Damian Crowther; Christopher Dobson (2008). "Protein misfolding and disease: from the test tube to the organism". Current Opinion in Chemical Biology. 12 (1): 25–31.
doi:
10.1016/j.cbpa.2008.02.011.
PMID 18295611.
^ C. D. Snow; E. J. Sorin; Y. M. Rhee; V. S. Pande. (2005). "How well can simulation predict protein folding kinetics and thermodynamics?". Annual Review of Biophysics (review). 34: 43–69.
doi:
10.1146/annurev.biophys.34.040204.144447.
PMID 15869383.
^ A. Verma; S.M. Gopal; A. Schug; J.S. Oh; K.V. Klenin; K.H. Lee; W. Wenzel (2008). Massively Parallel All Atom Protein Folding in a Single Day. Advances in Parallel Computing. 15. pp. 527–534.
ISBN 978-1-58603-796-3.
ISSN 0927-5452.
^ Vijay S. Pande; Ian Baker; Jarrod Chapman; Sidney P. Elmer; Siraj Khaliq; Stefan M. Larson; Young Min Rhee; Michael R. Shirts; Christopher D. Snow; Eric J. Sorin; Bojan Zagrovic (2002). "Atomistic protein folding simulations on the submillisecond timescale using worldwide distributed computing". Biopolymers. 68 (1): 91–109.
doi:
10.1002/bip.10219.
PMID 12579582.
^
Jump up to: a b c G. Bowman; V. Volez; V. S. Pande (2011).
"Taming the complexity of protein folding". Current Opinion in Structural Biology. 21 (1): 4–11.
doi:
10.1016/j.sbi.2010.10.006.
PMC 3042729.
PMID 21081274.
^ Chodera, John D.; Swope, William C.; Pitera, Jed W.; Dill, Ken A. (January 1, 2006).
"Long‐Time Protein Folding Dynamics from Short‐Time Molecular Dynamics Simulations". Multiscale Modeling & Simulation. 5 (4): 1214–1226.
doi:
10.1137/06065146X.
^ Robert B Best (2012). "Atomistic molecular simulations of protein folding". Current Opinion in Structural Biology (review). 22 (1): 52–61.
doi:
10.1016/j.sbi.2011.12.001.
PMID 22257762.
^
Jump up to: a b c TJ Lane; Gregory Bowman; Robert McGibbon; Christian Schwantes; Vijay Pande; Bruce Borden (September 10, 2012).
"Folding@home Simulation FAQ". Folding@home. foldingathome.org. Archived from
the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved July 8, 2013.
^ Gregory R. Bowman; Daniel L. Ensign; Vijay S. Pande (2010).
"Enhanced Modeling via Network Theory: Adaptive Sampling of Markov State Models". Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation. 6 (3): 787–794.
doi:
10.1021/ct900620b.
PMC 3637129.
PMID 23626502.
^ Vijay Pande (June 8, 2012).
"FAHcon 2012: Thinking about how far FAH has come". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved June 12, 2012.
^ Kyle A. Beauchamp; Daniel L. Ensign; Rhiju Das; Vijay S. Pande (2011).
"Quantitative comparison of villin headpiece subdomain simulations and triplet–triplet energy transfer experiments". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 108 (31): 12734–9.
Bibcode:
2011PNAS..10812734B.
doi:
10.1073/pnas.1010880108.
PMC 3150881.
PMID 21768345.
^ Timothy H. Click; Debabani Ganguly; Jianhan Chen (2010).
"Intrinsically Disordered Proteins in a Physics-Based World". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 11 (12): 919–27.
doi:
10.3390/ijms11125292.
PMC 3100817.
PMID 21614208.
^ "Greg Bowman awarded the 2010 Kuhn Paradigm Shift Award". simtk.org. SimTK: MSMBuilder. March 29, 2010.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 20,2012.
^ "MSMBuilder Source Code Repository". MSMBuilder. simtk.org. 2012.
Archived from the original on October 12, 2012. Retrieved October 12, 2012.
^ "Biophysical Society Names Five 2012 Award Recipients". Biophysics.org. Biophysical Society. August 17, 2011. Archived from
the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 20,2012.
^ "Folding@home – Awards". Folding@home. foldingathome.org. August 2011. Archived from
the original (FAQ) on September 21, 2012. Retrieved July 8, 2013.
^ Vittorio Bellotti; Monica Stoppini (2009).
"Protein Misfolding Diseases" (PDF). The Open Biology Journal. 2 (2): 228–234.
doi:
10.2174/1874196700902020228. Archived from the original on February 22, 2014.
^
Jump up to: a b c d e f g h i Pande lab (May 30, 2012).
"Folding@home Diseases Studied FAQ". Folding@home. foldingathome.org. Archived from
the original (FAQ) on September 21, 2012. Retrieved July 8, 2013.
^
Jump up to: a b Collier, Leslie; Balows, Albert; Sussman, Max (1998). Mahy, Brian; Collier, Leslie (eds.). Topley and Wilson's Microbiology and Microbial Infections. 1, Virology (ninth ed.). London: Arnold. pp. 75–91.
ISBN 978-0-340-66316-5.
^ Fred E. Cohen; Jeffery W. Kelly (2003). "Therapeutic approaches to protein misfolding diseases". Nature (review). 426 (6968): 905–9.
Bibcode:
2003Natur.426..905C.
doi:
10.1038/nature02265.
PMID 14685252.
^
Jump up to: a b Chun Song; Shen Lim; Joo Tong (2009). "Recent advances in computer-aided drug design". Briefings in Bioinformatics (review). 10 (5): 579–91.
doi:
10.1093/bib/bbp023.
PMID 19433475.
^
Jump up to: a b c d e f Pande lab (2012).
"Folding@Home Press FAQ". Folding@home. foldingathome.org. Archived from
the original (FAQ) on September 21, 2012. Retrieved July 8, 2013.
^ Christian "schwancr" Schwantes (Pande lab member) (August 15, 2011).
"Projects 7808 and 7809 to full fah". Folding@home.
phpBB Group.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved October 16, 2011.
^ Del Lucent; V. Vishal; Vijay S. Pande (2007).
"Protein folding under confinement: A role for solvent".
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 104(25): 10430–10434.
Bibcode:
2007PNAS..10410430L.
doi:
10.1073/pnas.0608256104.
PMC 1965530.
PMID 17563390.
^ Vincent A. Voelz; Vijay R. Singh; William J. Wedemeyer; Lisa J. Lapidus; Vijay S. Pande (2010).
"Unfolded-State Dynamics and Structure of Protein L Characterized by Simulation and Experiment". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 132 (13): 4702–4709.
doi:
10.1021/ja908369h.
PMC 2853762.
PMID 20218718.
^
Jump up to: a b Vijay Pande (April 23, 2008).
"Folding@home and Simbios". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved November 9, 2011.
^ Vijay Pande (October 25, 2011).
"Re: Suggested Changes to F@h Website". Folding@home.
phpBB Group.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved October 25, 2011.
^ Caroline Hadley (2004).
"Biologists think bigger". EMBO Reports. 5 (3): 236–238.
doi:
10.1038/sj.embor.7400108.
PMC 1299019.
PMID 14993921.
^ S. Pronk; P. Larsson; I. Pouya; G.R. Bowman; I.S. Haque; K. Beauchamp; B. Hess; V.S. Pande; P.M. Kasson; E. Lindahl (2011). "Copernicus: A new paradigm for parallel adaptive molecular dynamics". 2011 International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage and Analysis: 1–10, 12–18.
^ Sander Pronk; Iman Pouya; Per Larsson; Peter Kasson; Erik Lindahl (November 17, 2011).
"Copernicus Download". copernicus-computing.org. Copernicus.
Archived from the original on October 12, 2012. Retrieved October 2, 2012.
^ Pande lab (July 27, 2012).
"Papers & Results from Folding@home". Folding@home. foldingathome.org.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved 1 February 2019.
^ G Brent Irvine; Omar M El-Agnaf; Ganesh M Shankar; Dominic M Walsh (2008).
"Protein Aggregation in the Brain: The Molecular Basis for Alzheimer's and Parkinson's Diseases". Molecular Medicine (review). 14 (7–8): 451–464.
doi:
10.2119/2007-00100.Irvine.
PMC 2274891.
PMID 18368143.
^ Claudio Soto; Lisbell D. Estrada (2008). "Protein Misfolding and Neurodegeneration". Archives of Neurology (review). 65 (2): 184–189.
doi:
10.1001/archneurol.2007.56.
PMID 18268186.
^ Robin Roychaudhuri; Mingfeng Yang; Minako M. Hoshi; David B. Teplow (2008).
"Amyloid β-Protein Assembly and Alzheimer Disease". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 284 (8): 4749–53.
doi:
10.1074/jbc.R800036200.
PMC 3837440.
PMID 18845536.
^
Jump up to: a b Nicholas W. Kelley; V. Vishal; Grant A. Krafft; Vijay S. Pande. (2008).
"Simulating oligomerization at experimental concentrations and long timescales: A Markov state model approach". Journal of Chemical Physics. 129 (21): 214707.
Bibcode:
2008JChPh.129u4707K.
doi:
10.1063/1.3010881.
PMC 2674793.
PMID 19063575.
^
Jump up to: a b P. Novick, J. Rajadas, C.W. Liu, N. W. Kelley, M. Inayathullah, and V. S. Pande (2011). Buehler, Markus J. (ed.).
"Rationally Designed Turn Promoting Mutation in the Amyloid-β Peptide Sequence Stabilizes Oligomers in Solution". PLOS ONE. 6 (7): e21776.
Bibcode:
2011PLoSO...621776R.
doi:
10.1371/journal.pone.0021776.
PMC 3142112.
PMID 21799748.
^ Aabgeena Naeem; Naveed Ahmad Fazili (2011). "Defective Protein Folding and Aggregation as the Basis of Neurodegenerative Diseases: The Darker Aspect of Proteins".
Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics (review). 61 (2): 237–50.
doi:
10.1007/s12013-011-9200-x.
PMID 21573992.
^
Jump up to: a b c d Gregory R Bowman; Xuhui Huang; Vijay S Pande (2010).
"Network models for molecular kinetics and their initial applications to human health". Cell Research (review). 20 (6): 622–630.
doi:
10.1038/cr.2010.57.
PMC 4441225.
PMID 20421891.
^ Vijay Pande (December 18, 2008).
"New FAH results on possible new Alzheimer's drug presented". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 23, 2011.
^ Paul A. Novick; Dahabada H. Lopes; Kim M. Branson; Alexandra Esteras-Chopo; Isabella A. Graef; Gal Bitan; Vijay S. Pande (2012).
"Design of β-Amyloid Aggregation Inhibitors from a Predicted Structural Motif". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 55 (7): 3002–10.
doi:
10.1021/jm201332p.
PMC 3766731.
PMID 22420626.
^ yslin (Pande lab member) (July 22, 2011).
"New project p6871 [Classic]". Folding@home.
phpBB Group.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved March 17, 2012.(
registration required)
^ Pande lab.
"Project 6871 Description". Folding@home. foldingathome.org.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 27, 2011.
^ Walker FO (2007). "Huntington's disease". Lancet. 369 (9557): 218–28 [220].
doi:
10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60111-1.
PMID 17240289.
^ Nicholas W. Kelley; Xuhui Huang; Stephen Tam; Christoph Spiess; Judith Frydman; Vijay S. Pande (2009).
"The predicted structure of the headpiece of the Huntingtin protein and its implications on Huntingtin aggregation". Journal of Molecular Biology. 388 (5): 919–27.
doi:
10.1016/j.jmb.2009.01.032.
PMC 2677131.
PMID 19361448.
^ Susan W Liebman; Stephen C Meredith (2010). "Protein folding: Sticky N17 speeds huntingtin pile-up". Nature Chemical Biology. 6 (1): 7–8.
doi:
10.1038/nchembio.279.
PMID 20016493.
^ Diwakar Shukla (Pande lab member) (February 10, 2012).
"Project 8021 released to beta". Folding@home.
phpBB Group.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved March 17, 2012.(
registration required)
^ M Hollstein; D Sidransky; B Vogelstein; CC Harris (1991).
"p53 mutations in human cancers". Science. 253 (5015): 49–53.
Bibcode:
1991Sci...253...49H.
doi:
10.1126/science.1905840.
PMID 1905840.
^ L. T. Chong; C. D. Snow; Y. M. Rhee; V. S. Pande. (2004). "Dimerization of the p53 Oligomerization Domain: Identification of a Folding Nucleus by Molecular Dynamics Simulations". Journal of Molecular Biology. 345 (4): 869–878.
CiteSeerX 10.1.1.132.1174.
doi:
10.1016/j.jmb.2004.10.083.
PMID 15588832.
^ mah3, Vijay Pande (September 24, 2004).
"F@H project publishes results of cancer related research".
MaximumPC.com. Future US, Inc.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 20, 2012. To our knowledge, this is the first peer-reviewed results from a distributed computing project related to cancer.
^ Lillian T. Chong; William C. Swope; Jed W. Pitera; Vijay S. Pande (2005). "Kinetic Computational Alanine Scanning: Application to p53 Oligomerization". Journal of Molecular Biology. 357 (3): 1039–1049.
doi:
10.1016/j.jmb.2005.12.083.
PMID 16457841.
^ Almeida MB, do Nascimento JL, Herculano AM, Crespo-López ME (2011). "Molecular chaperones: toward new therapeutic tools". Journal of Molecular Biology (review). 65 (4): 239–43.
doi:
10.1016/j.biopha.2011.04.025.
PMID 21737228.
^ Vijay Pande (September 28, 2007).
"Nanomedicine center". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 23, 2011.
^ Vijay Pande (December 22, 2009).
"Release of new Protomol (Core B4) WUs". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 23, 2011.
^ Pande lab.
"Project 180 Description". Folding@home. foldingathome.org.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 27, 2011.
^ TJ Lane (Pande lab member) (June 8, 2011).
"Project 7600 in Beta". Folding@home.
phpBBGroup.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 27, 2011.(
registration required)
^ TJ Lane (Pande lab member) (June 8, 2011).
"Project 7600 Description". Folding@home. foldingathome.org.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved March 31, 2012.
^ "Scientists boost potency, reduce side effects of IL-2 protein used to treat cancer". MedicalXpress.com. Medical Xpress. March 18, 2012.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 20, 2012.
^ Aron M. Levin; Darren L. Bates; Aaron M. Ring; Carsten Krieg; Jack T. Lin; Leon Su; Ignacio Moraga; Miro E. Raeber; Gregory R. Bowman; Paul Novick; Vijay S. Pande; C. Garrison Fathman; Onur Boyman; K. Christopher Garcia (2012).
"Exploiting a natural conformational switch to engineer an interleukin-2 'superkine'". Nature. 484 (7395): 529–33.
Bibcode:
2012Natur.484..529L.
doi:
10.1038/nature10975.
PMC 3338870.
PMID 22446627.
^ Rauch F, Glorieux FH (2004). "Osteogenesis imperfecta". Lancet. 363 (9418): 1377–85.
doi:
10.1016/S0140-6736(04)16051-0.
PMID 15110498.
^ Fratzl, Peter (2008).
Collagen: structure and mechanics.
ISBN 978-0-387-73905-2. Retrieved March 17, 2012.
^ Gautieri A, Uzel S, Vesentini S, Redaelli A, Buehler MJ (2009).
"Molecular and mesoscale disease mechanisms of Osteogenesis Imperfecta". Biophysical Journal. 97 (3): 857–865.
Bibcode:
2009BpJ....97..857G.
doi:
10.1016/j.bpj.2009.04.059.
PMC 2718154.
PMID 19651044.
^ Sanghyun Park; Randall J. Radmer; Teri E. Klein; Vijay S. Pande (2005). "A New Set of Molecular Mechanics Parameters for Hydroxyproline and Its Use in Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Collagen-Like Peptides". Journal of Computational Chemistry. 26 (15): 1612–1616.
CiteSeerX 10.1.1.142.6781.
doi:
10.1002/jcc.20301.
PMID 16170799.
^ Gregory Bowman (Pande lab Member).
"Project 10125". Folding@home.
phpBB Group. Retrieved December 2, 2011.(
registration required)
^ Hana Robson Marsden; Itsuro Tomatsu; Alexander Kros (2011). "Model systems for membrane fusion". Chemical Society Reviews (review). 40 (3): 1572–1585.
doi:
10.1039/c0cs00115e.
PMID 21152599.
^ Peter Kasson (2012).
"Peter M. Kasson". Kasson lab.
University of Virginia. Archived from
the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 20, 2012.
^ Peter M. Kasson; Afra Zomorodian; Sanghyun Park; Nina Singhal; Leonidas J. Guibas; Vijay S. Pande (2007). "Persistent voids: a new structural metric for membrane fusion". Bioinformatics. 23(14): 1753–1759.
doi:
10.1093/bioinformatics/btm250.
PMID 17488753.
^ Peter M. Kasson; Daniel L. Ensign; Vijay S. Pande (2009).
"Combining Molecular Dynamics with Bayesian Analysis To Predict and Evaluate Ligand-Binding Mutations in Influenza Hemagglutinin". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 131 (32): 11338–11340.
doi:
10.1021/ja904557w.
PMC 2737089.
PMID 19637916.
^ Peter M. Kasson; Vijay S. Pande (2009).
"Combining mutual information with structural analysis to screen for functionally important residues in influenza hemagglutinin". Pacific Symposium on Biocomputing: 492–503.
doi:
10.1142/9789812836939_0047.
ISBN 978-981-283-692-2.
PMC 2811693.
PMID 19209725.
^ Vijay Pande (February 24, 2012).
"Protein folding and viral infection". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved March 4, 2012.
^ Broekhuijsen, Niels (March 3, 2020).
"Help Cure Coronavirus with Your PC's Leftover Processing Power". Tom's Hardware. Retrieved March 12, 2020.
^ Bowman, Greg (February 27, 2020).
"Folding@home takes up the fight against COVID-19 / 2019-nCoV". Folding@home. Retrieved March 12, 2020.
^ "Folding@home Turns Its Massive Crowdsourced Computer Network Against COVID-19". March 16, 2020.
^ Vijay Pande (February 27, 2012).
"New methods for computational drug design". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved April 1, 2012.
^ Guha Jayachandran; M. R. Shirts; S. Park; V. S. Pande (2006). "Parallelized-Over-Parts Computation of Absolute Binding Free Energy with Docking and Molecular Dynamics". Journal of Chemical Physics. 125 (8): 084901.
Bibcode:
2006JChPh.125h4901J.
doi:
10.1063/1.2221680.
PMID 16965051.
^ Pande lab.
"Project 10721 Description". Folding@home. foldingathome.org.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 27, 2011.
^
Jump up to: a b Gregory Bowman (July 23, 2012).
"Searching for new drug targets". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 27, 2011.
^ Gregory R. Bowman; Phillip L. Geissler (July 2012).
"Equilibrium fluctuations of a single folded protein reveal a multitude of potential cryptic allosteric sites".
PNAS. 109 (29): 11681–6.
Bibcode:
2012PNAS..10911681B.
doi:
10.1073/pnas.1209309109.
PMC 3406870.
PMID 22753506.
^ Paula M. Petrone; Christopher D. Snow; Del Lucent; Vijay S. Pande (2008).
"Side-chain recognition and gating in the ribosome exit tunnel". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 105 (43): 16549–54.
Bibcode:
2008PNAS..10516549P.
doi:
10.1073/pnas.0801795105.
PMC 2575457.
PMID 18946046.
^ Pande lab.
"Project 5765 Description". Folding@home. foldingathome.org.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved December 2, 2011.
^ National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (August 21, 2018).
"Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease Fact Sheet". NIH. Retrieved March 2, 2019.
^
Jump up to: a b c d e f Kupfer, L; Hinrichs, W; Groschup, M.H. (2009).
"Prion Protein Misfolding". Current Molecular Medicine. Bentham Science Publishers. 9 (7): 826–835.
doi:
10.2174/156652409789105543.
PMC 3330701.
PMID 19860662.
^
Jump up to: a b c Riek, Poland; Hornemann, Simone; Wider, Gerhard; Billeter, Martin; Glockshuber, Rudi; Wüthrich, Kurt (1996). "NMR structure of the mouse prion protein domain in PrP(121-231)". Nature. Nature Research. 382 (6587): 180–182.
Bibcode:
1996Natur.382..180R.
doi:
10.1038/382180a0.
PMID 8700211.
^
Jump up to: a b Ziegler, J; Sticht, H; Marx, UC; Müller, W; Rösch, P; Schwarzinger, S (2003).
"CD and NMR studies of prion protein (PrP) helix1. Novel implications for its role in the PrPC-->PrPSc conversion process" (PDF). J Biol Chem. American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 278 (50): 50175–81.
doi:
10.1074/jbc.M305234200.
PMID 12952977.
^ Govaerts, Cedric; Wile, Holger; Brusiner, Stanley B.; Cohen, Fred (2004).
"Evidence for assembly of prions with left-handed β-helices into trimers". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. National Academy of Sciences. 101 (22): 8342–47.
Bibcode:
2004PNAS..101.8342G.
doi:
10.1073/pnas.0402254101.
PMC 420396.
PMID 15155909.
^ Silveira, Jay; Raymond, Gregory; Hughson, Andrew; Race, Richard; Sim, Valerie; Caughey, Byron; Hayes, Stanley (2005).
"The most infectious prion protein particles". Nature. Nature Research. 437 (7056): 257–261.
Bibcode:
2005Natur.437..257S.
doi:
10.1038/nature03989.
PMC 1513539.
PMID 16148934.
^
Jump up to: a b Moore, Roger A.; Taubner, Lara M.; Priola, Suzette (2009).
"Prion Protein Misfolding and Disease". Curr Opin Struct Biol. Elsevier. 19 (1): 14–22.
doi:
10.1016/j.sbi.2008.12.007.
PMC 2674794.
PMID 19157856.
^ Moore, Roger A.; Herzog, Christian; Errett, John; Kocisko, David A.; Arnold, Kevin M.; Hayes, Stanley F.; Priola, Suzette A. (2006).
"Octapeptide repeat insertions increase the rate of protease-resistant prion protein formation". Protein Science. Wiley-Blackwell. 15 (3): 609–619.
doi:
10.1110/ps.051822606.
PMC 2249780.
PMID 16452616.
^ Gasset, M; Baldwin, M; Lloyd, D; Gabriel, J; Holtzman, D; Cohen, F; Fletterick, R; Brusiner, S (1992).
"Predicted alpha-helical regions of the prion protein when synthesized as peptides form amyloid". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. National Academy of Sciences. 89 (22): 10940–44.
Bibcode:
1992PNAS...8910940G.
doi:
10.1073/pnas.89.22.10940.
PMC 50458.
PMID 1438300.
^ Ziegler, Jan; Viehrig, Christine; Geimer, Stefan; Rosch, Paul; Schwarzinger, Stephan (2006). "Putative aggregation initiation sites in prion protein". FEBS Letters. FEBS Press. 580 (8): 2033–40.
doi:
10.1016/j.febslet.2006.03.002.
PMID 16545382.
^ Brusiner, Stanley (1998).
"Prions". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. National Academy of Sciences. 95(23): 13363–83.
Bibcode:
1998PNAS...9513363P.
doi:
10.1073/pnas.95.23.13363.
PMC 33918.
PMID 9811807.
^ Vorberg, I; Groschup, MH; Pfaff, E; Priola, SA (2003).
"Multiple amino acid residues within the rabbit prion protein inhibit formation of its abnormal isoform". J. Virol. American Society for Microbiology. 77 (3): 2003–9.
doi:
10.1128/JVI.77.3.2003-2009.2003.
PMC 140934.
PMID 12525634.
^ Barrow, CJ; Yasuda, A; Kenny, PT; Zagorski, MG (1992). "Solution conformations and aggregational properties of synthetic amyloid beta-peptides of Alzheimer's disease. Analysis of circular dichroism spectra". J Biol Chem. American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 225 (4): 1075–93.
doi:
10.1016/0022-2836(92)90106-t.
PMID 1613791.
^ Kuznetsov, Igor; Rackovsky, Shalom (2004).
"Comparative computational analysis of prion proteins reveals two fragments with unusual structural properties and a pattern of increase in hydrophobicity associated with disease-promoting mutations". Protein Science. Wiley-Blackwell. 13 (12): 3230–44.
doi:
10.1110/ps.04833404.
PMC 2287303.
PMID 15557265.
^ Baskakov, IV; Legname, G; Baldwin, MA; Prusiner, SB; Cohen, FE (2002). "Pathway complexity of prion protein assembly into amyloid". J Biol Chem. American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. 277 (24): 21140–8.
doi:
10.1074/jbc.M111402200.
PMID 11912192.
^ Raddick, M. Jordan; Bracey, Georgia; Gay, Pamela L.; Lintott, Chris J.; Murray, Phil; Schawinski, Kevin; Szalay, Alexander S.; Vandenberg, Jan (December 2010). "Galaxy Zoo: Exploring the Motivations of Citizen Science Volunteers". Astronomy Education Review. 9 (1): 010103.
arXiv:
0909.2925.
Bibcode:
2010AEdRv...9a0103R.
doi:
10.3847/AER2009036.
^ Vickie, Curtis (April 20, 2018). Online citizen science and the widening of academia : distributed engagement with research and knowledge production. Cham, Switzerland.
ISBN 9783319776644.
OCLC 1034547418.
^ Nov, Oded; Arazy, Ofer; Anderson, David (2011).
"Dusting for science: motivation and participation of digital citizen science volunteers". Proceedings of the 2011 IConference on - IConference '11. IConference '11. Seattle, Washington: ACM Press: 68–74.
doi:
10.1145/1940761.1940771.
ISBN 9781450301213.
^ Curtis, Vickie (December 2015).
"Motivation to Participate in an Online Citizen Science Game: A Study of Foldit" (PDF). Science Communication. 37 (6): 723–746.
doi:
10.1177/1075547015609322.
ISSN 1075-5470.
^
Jump up to: a b c Curtis, Vickie (April 27, 2018). "Patterns of Participation and Motivation in Folding@home: The Contribution of Hardware Enthusiasts and Overclockers". Citizen Science: Theory and Practice. 3 (1): 5.
doi:
10.5334/cstp.109.
ISSN 2057-4991.
^ Colwell, B. (March 2004). "The Zen of overclocking". Computer. 37 (3): 9–12.
doi:
10.1109/MC.2004.1273994.
ISSN 0018-9162.
^ Kloetzer, Laure; Da Costa, Julien; Schneider, Daniel K. (December 31, 2016). "Not so passive: engagement and learning in Volunteer Computing projects". Human Computation. 3 (1).
doi:
10.15346/hc.v3i1.4.
ISSN 2330-8001.
^ Darch Peter; Carusi Annamaria (September 13, 2010). "Retaining volunteers in volunteer computing projects". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences. 368 (1926): 4177–4192.
Bibcode:
2010RSPTA.368.4177D.
doi:
10.1098/rsta.2010.0163.
PMID 20679130.
^ "2013 Member Study: Findings and Next Steps". World Community Grid.
^ Krebs, Viola (January 31, 2010). "Motivations of cybervolunteers in an applied distributed computing environment: MalariaControl.net as an example". First Monday. 15 (2).
doi:
10.5210/fm.v15i2.2783.
^ Curtis, Vickie (2015).
Online citizen science projects: an exploration of motivation, contribution and participation, PhD Thesis (PDF). United Kingdom: The Open University.
^ Mims 2010
^ Pande 2008: "Wall clock time is in the end the only thing that matters and that's why we benchmark on wall clock (and why in our papers, we emphasize wall clock)."
^ Vijay Pande (September 16, 2007).
"Crossing the petaFLOPS barrier". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved August 28, 2011.
^
Jump up to: a b Michael Gross (2012). "Folding research recruits unconventional help". Current Biology. 22 (2): R35–R38.
doi:
10.1016/j.cub.2012.01.008.
PMID 22389910.
^ "TOP500 List — June 2007". top500.org.
Top500. June 2007. Retrieved September 20, 2012.
^ "Folding@Home reach 2 Petaflops". n4g.com. HAVAmedia. May 8, 2008.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 20, 2012.
^ "NVIDIA Achieves Monumental Folding@Home Milestone With Cuda". nvidia.com.
NVIDIA Corporation. August 26, 2008. Retrieved September 20, 2012.
^ "3 PetaFLOP barrier". longecity.org. Longecity. August 19, 2008.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 20, 2012.
^ "Increase in 'active' PS3 folders pushes Folding@home past 4 Petaflops!". team52735.blogspot.com.
Blogspot. September 29, 2008.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 20, 2012.
^ Vijay Pande (February 18, 2009).
"Folding@home Passes the 5 petaFLOP Mark". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved August 31, 2011.
^ "Crossing the 5 petaFLOPS barrier". longecity.org. Longecity. February 18, 2009.
Archivedfrom the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 20, 2012.
^ Dragan Zakic (May 2009).
"Community Grid Computing — Studies in Parallel and Distributed Systems" (PDF). Massey University College of Sciences.
Massey University. Archived from
the original (PDF) on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 20, 2012.
^ William Ito.
"A review of recent advances in ab initio protein folding by the Folding@home project" (PDF). foldingathome.org. Archived from
the original (PDF) on September 22, 2012. Retrieved September 22, 2012.
^ "TOP500 List — November 2008". top500.org.
Top500. November 2008. Retrieved September 20, 2012.
^ Jesse Victors (November 10, 2011).
"Six Native PetaFLOPS". Folding@home.
phpBB Group.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved November 11, 2011.
^ Risto Kantonen (September 23, 2013).
"Folding@home Stats - Google Docs". Folding@home. Retrieved September 23, 2013.
^ "100 Petaflops nearly reached". foldingathome.org. May 11, 2016. Retrieved August 9, 2016.
^ Bowman, Greg (March 20, 2020).
"Amazing! @foldingathome now has over 470 petaFLOPS of compute power. To put that in perspective, that's more than 2x the peak performance of the Summit super computer!". @drGregBowman. Retrieved March 20, 2020.
^ "Folding@home stats report". March 20, 2020. Archived from
the original on March 20, 2020. Retrieved March 20, 2020.
^ Shilov, Anton (March 25, 2020).
"Folding@Home Reaches Exascale: 1,500,000,000,000,000,000 Operations Per Second for COVID-19".
Anandtech. Retrieved March 26, 2020.
^
Jump up to: a b c d e Pande lab (August 20, 2012).
"Folding@home Points FAQ". Folding@home. foldingathome.org. Archived from
the original (FAQ) on September 21, 2012. Retrieved July 8,2013.
^ Pande lab (July 23, 2012).
"Folding@home Passkey FAQ". Folding@home. foldingathome.org. Archived from
the original (FAQ) on September 21, 2012. Retrieved July 8, 2013.
^
Jump up to: a b Peter Kasson (Pande lab member) (January 24, 2010).
"upcoming release of SMP2 cores". Folding@home.
phpBB Group.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 30, 2011.
^
Jump up to: a b c d e Pande lab (August 18, 2011).
"Folding@home Main FAQ" (FAQ). Folding@home. foldingathome.org.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved July 8, 2013.
^ "Official Extreme Overclocking Folding@home Team Forum". forums.extremeoverclocking.com. Extreme Overclocking.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 20, 2012.
^
Jump up to: a b c d e f g Adam Beberg; Daniel Ensign; Guha Jayachandran; Siraj Khaliq; Vijay Pande (2009).
"Folding@home: Lessons from eight years of volunteer distributed computing" (PDF). 2009 IEEE International Symposium on Parallel & Distributed Processing. Proceedings. pp. 1–8.
doi:
10.1109/IPDPS.2009.5160922.
ISBN 978-1-4244-3751-1.
ISSN 1530-2075.
^ Norman Chan (April 6, 2009).
"Help Maximum PC's Folding Team Win the Next Chimp Challenge!". Maximumpc.com. Future US, Inc.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 20, 2012.
^
Jump up to: a b c Pande lab (June 11, 2012).
"Folding@home SMP FAQ". Folding@home. foldingathome.org. Archived from
the original (FAQ) on September 21, 2012. Retrieved July 8,2013.
^ Vijay Pande (April 5, 2011).
"More transparency in testing". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved October 14, 2011.
^ Bruce Borden (August 7, 2011).
"Re: Gromacs Cannot Continue Further". Folding@home.
phpBB Group.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved August 7, 2011.
^ PantherX (October 1, 2011).
"Re: Project 6803: (Run 4, Clone 66, Gen 255)". Folding@home.
phpBB Group.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved October 9, 2011.
^ PantherX (October 31, 2010).
"Troubleshooting Bad WUs". Folding@home.
phpBB Group.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved August 7, 2011.
^ Carsten Kutzner; David Van Der Spoel; Martin Fechner; Erik Lindahl; Udo W. Schmitt; Bert L. De Groot; Helmut Grubmüller (2007). "Speeding up parallel GROMACS on high-latency networks". Journal of Computational Chemistry. 28 (12): 2075–2084.
doi:
10.1002/jcc.20703.
hdl:
11858/00-001M-0000-0012-E29A-0.
PMID 17405124.
^ Berk Hess; Carsten Kutzner; David van der Spoel; Erik Lindahl (2008). "GROMACS 4: Algorithms for Highly Efficient, Load-Balanced, and Scalable Molecular Simulation". Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation. 4 (3): 435–447.
doi:
10.1021/ct700301q.
hdl:
11858/00-001M-0000-0012-DDBF-0.
PMID 26620784.
^ Pande lab (August 19, 2012).
"Folding@home Gromacs FAQ". Folding@home. foldingathome.org. Archived from
the original (FAQ) on September 21, 2012. Retrieved July 8,2013.
^ Pande lab (August 7, 2012).
"Folding@home Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) Index". Folding@home. foldingathome.org. Archived from
the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved July 8, 2013.
^ Vijay Pande (September 25, 2009).
"Update on new FAH cores and clients". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved February 24, 2012.
^
Jump up to: a b M. S. Friedrichs; P. Eastman; V. Vaidyanathan; M. Houston; S. LeGrand; A. L. Beberg; D. L. Ensign; C. M. Bruns; V. S. Pande (2009).
"Accelerating Molecular Dynamic Simulation on Graphics Processing Units". Journal of Computational Chemistry. 30 (6): 864–72.
doi:
10.1002/jcc.21209.
PMC 2724265.
PMID 19191337.
^ Pande lab (August 19, 2012).
"Folding@home Petaflop Initiative". Folding@home. foldingathome.org. Archived from
the original (FAQ) on September 21, 2012. Retrieved July 8,2013.
^
Jump up to: a b Pande lab (February 10, 2011).
"Windows Uniprocessor Client Installation Guide". Folding@home. foldingathome.org. Archived from
the original (Guide) on September 21, 2012. Retrieved July 8, 2013.
^ PantherX (September 2, 2010).
"Re: Can Folding@home damage any part of my PC?". Folding@home.
phpBB Group.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved February 25, 2012.
^
Jump up to: a b c Vijay Pande (June 17, 2009).
"How does FAH code development and sysadmin get done?". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved October 14, 2011.
^
Jump up to: a b Pande lab (May 30, 2012).
"Uninstalling Folding@home Guide". Folding@home. foldingathome.org. Archived from
the original (Guide) on September 21, 2012. Retrieved July 8,2013.
^
Jump up to: a b Folding@home developers.
"FAHControl source code repository". foldingathome.org. Archived from
the original on December 12, 2012. Retrieved October 15, 2012.
^ Pande lab.
"Folding@home Distributed Computing Client". Folding@home. foldingathome.org. Archived from
the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved July 8, 2013.
^ Vijay Pande (June 28, 2008).
"Folding@home's End User License Agreement (EULA)". Folding@home.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved May 15, 2012.
^ unikuser (August 7, 2011).
"FoldingAtHome". Ubuntu Documentation. help.ubuntu.com.
Archived from the original on September 22, 2012. Retrieved September 22, 2012.
^ "The Case of the Modified Binaries". Leviathan Security.
^ "Fixing/Making Holes in ELF Binaries/Programs - Black Hat".
^ probably using tools such as
ERESI
^ "x86 - How to disassemble, modify and then reassemble a Linux executable?". Stack Overflow.
^ "linux - How do I add functionality to an existing binary executable?". Reverse Engineering Stack Exchange.
^ "Certificate Bypass: Hiding and Executing Malware from a Digitally Signed Executable" (PDF). BlackHat.com.
Deep Instinct. August 2016.
^ Phineus R. L. Markwick; J. Andrew McCammon (2011). "Studying functional dynamics in bio-molecules using accelerated molecular dynamics". Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 13 (45): 20053–65.
Bibcode:
2011PCCP...1320053M.
doi:
10.1039/C1CP22100K.
PMID 22015376.
^ M. R. Shirts; V. S. Pande. (2000).
"Screen Savers of the World, Unite!". Science. 290 (5498): 1903–1904.
doi:
10.1126/science.290.5498.1903.
PMID 17742054.
^ Pande lab.
"Folding@Home Executive summary" (PDF). Folding@home. foldingathome.org.
Archived (PDF) from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved October 4, 2011.
^ Rattledagger, Vijay Pande (April 1, 2005).
"Folding@home client for BOINC in beta "soon"". Boarddigger.com. Anandtech.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 20, 2012.
^
Jump up to: a b c Pande lab (May 30, 2012).
"High Performance FAQ". Folding@home. foldingathome.org. Archived from
the original (FAQ) on September 21, 2012. Retrieved July 8, 2013.
^ John D. Owens; David Luebke; Naga Govindaraju; Mark Harris; Jens Krüger; Aaron Lefohn; Timothy J. Purcell (2007). "A Survey of General-Purpose Computation on Graphics Hardware". Computer Graphics Forum. 26 (1): 80–113.
CiteSeerX 10.1.1.215.426.
doi:
10.1111/j.1467-8659.2007.01012.x.
^ P. Eastman; V. S. Pande (2010).
"OpenMM: A Hardware-Independent Framework for Molecular Simulations". Computing in Science and Engineering. 12 (4): 34–39.
Bibcode:
2010CSE....12d..34E.
doi:
10.1109/MCSE.2010.27.
ISSN 1521-9615.
PMC 4486654.
PMID 26146490.
^ I. Haque; V. S. Pande (2010). "Hard Data on Soft Errors: A Large-Scale Assessment of Real-World Error Rates in GPGPU". 2010 10th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Cluster, Cloud and Grid Computing. pp. 691–696.
arXiv:
0910.0505.
doi:
10.1109/CCGRID.2010.84.
ISBN 978-1-4244-6987-1.
^
Jump up to: a b c Pande lab (March 18, 2011).
"ATI FAQ". Folding@home. foldingathome.org. Archived from
the original (FAQ) on September 21, 2012. Retrieved July 8, 2013.
^ Vijay Pande (May 23, 2008).
"GPU news (about GPU1, GPU2, & NVIDIA support)". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 8, 2011.
^ Travis Desell; Anthony Waters; Malik Magdon-Ismail; Boleslaw K. Szymanski; Carlos A. Varela; Matthew Newby; Heidi Newberg; Andreas Przystawik; David Anderson (2009). "Accelerating the MilkyWay@Home volunteer computing project with GPUs". 8th International Conference on Parallel Processing and Applied Mathematics (PPAM 2009) Part I. pp. 276–288.
CiteSeerX 10.1.1.158.7614.
ISBN 978-3-642-14389-2.
^ Vijay Pande (April 10, 2008).
"GPU2 open beta". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archivedfrom the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 7, 2011.
^ Vijay Pande (April 15, 2008).
"Updates to the Download page/GPU2 goes live". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 7, 2011.
^ Vijay Pande (April 11, 2008).
"GPU2 open beta going well". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 7, 2011.
^
Jump up to: a b Vijay Pande (April 24, 2010).
"Prepping for the GPU3 rolling: new client and NVIDIA FAH GPU clients will (in the future) need CUDA 2.2 or later". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 8, 2011.
^ Vijay Pande (May 25, 2010).
"Folding@home: Open beta release of the GPU3 client/core". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 7, 2011.
^ Joseph Coffland (CEO of Cauldron Development LLC & lead developer at Folding@home) (October 13, 2011).
"Re: FAHClient V7.1.38 released (4th Open-Beta)". Folding@home.
phpBBGroup.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved October 15, 2011.
^ "NVIDIA GPU3 Linux/Wine Headless Install Guide". Folding@home.
phpBB Group. November 8, 2008.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 5, 2011.
^ Pande lab.
"Client Statistics by OS". Folding@home. foldingathome.org.
Archived from the original on November 28, 2012. Retrieved July 8, 2013.
^ Bruce Borden (June 25, 2013).
"GPU FahCore_17 is now available on Windows & native Linux". Folding@home.
phpBB Group. Retrieved September 30, 2014.
^ "Futures in Biotech 27: Folding@home at 1.3 Petaflops". Castroller.com. CastRoller. December 28, 2007. Archived from
the original (Interview, webcast) on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 20, 2012.
^
Jump up to: a b Edgar Luttmann; Daniel L. Ensign; Vishal Vaidyanathan; Mike Houston; Noam Rimon; Jeppe Øland; Guha Jayachandran; Mark Friedrichs; Vijay S. Pande (2008). "Accelerating Molecular Dynamic Simulation on the Cell processor and PlayStation 3". Journal of Computational Chemistry. 30 (2): 268–274.
doi:
10.1002/jcc.21054.
PMID 18615421.
^
Jump up to: a b David E. Williams (October 20, 2006).
"PlayStation's serious side: Fighting disease". CNN.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 20, 2012.
^ Jerry Liao (March 23, 2007).
"The Home Cure: PlayStation 3 to Help Study Causes of Cancer". mb.com. Manila Bulletin Publishing Corporation. Archived from
the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 20, 2012.
^ Lou Kesten,
Associated Press (March 26, 2007).
"Week in video-game news: 'God of War II' storms the PS2; a PS3 research project". Post-Gazette.com.
Pittsburgh Post-Gazette.
Archivedfrom the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 20, 2012.
^ Elaine Chow (September 18, 2008).
"PS3 News Service, Life With Playstation, Now Up For Download". Gizmodo.com.
Gizmodo.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 20, 2012.
^ Vijay Pande (September 18, 2008).
"Life with Playstation – a new update to the FAH/PS3 client". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved February 24, 2012.
^ Pande lab (May 30, 2012).
"PS3 FAQ". Folding@home. foldingathome.org. Archived from
the original (FAQ) on September 21, 2012. Retrieved July 8, 2013.
^ Eric Lempel (October 21, 2012).
"PS3 System Software Update (v4.30)". PlayStation blog.
Sony.
Archived from the original on October 22, 2012. Retrieved October 21, 2012.
^ "Termination of Life with PlayStation". Life with PlayStation.
Sony. November 6, 2012. Archived from
the original on November 9, 2012. Retrieved November 8, 2012.
^
Jump up to: a b Vijay Pande (June 15, 2008).
"What does the SMP core do?". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 7, 2011.
^ Daniel L. Ensign; Peter M. Kasson; Vijay S. Pande (2007).
"Heterogeneity Even at the Speed Limit of Folding: Large-scale Molecular Dynamics Study of a Fast-folding Variant of the Villin Headpiece". Journal of Molecular Biology. 374 (3): 806–816.
doi:
10.1016/j.jmb.2007.09.069.
PMC 3689540.
PMID 17950314.
^
Jump up to: a b Vijay Pande (March 8, 2008).
"New Windows client/core development (SMP and classic clients)". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 30, 2011.
^
Jump up to: a b Peter Kasson (Pande lab member) (July 15, 2009).
"new release: extra-large work units". Folding@home.
phpBB Group.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved October 9, 2011.
^ Vijay Pande (February 7, 2012).
"Update on "bigadv-16", the new bigadv rollout". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved February 9, 2012.
^ Vijay Pande (July 2, 2011).
"Change in the points system for bigadv work units". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved February 24, 2012.
^ Vijay Pande (January 15, 2014).
"Revised plans for BigAdv (BA) experiment". Retrieved October 6, 2014.
^
Jump up to: a b Pande lab (March 23, 2012).
"Windows (FAH V7) Installation Guide". Folding@home. foldingathome.org. Archived from
the original (Guide) on September 21, 2012. Retrieved July 8,2013.
^
Jump up to: a b c Vijay Pande (March 29, 2011).
"Client version 7 now in open beta". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved August 14, 2011.
^ Vijay Pande (March 22, 2012).
"Web page revamp and v7 rollout". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved March 22, 2012.
^ Vijay Pande (March 31, 2011).
"Core 16 for ATI released; also note on NVIDIA GPU support for older boards". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 7, 2011.
^ aschofield and jcoffland (October 3, 2011).
"Ticket #736 (Link to GPL in FAHControl)". Folding@home.
Trac. Archived from
the original on October 12, 2012. Retrieved October 12,2012.
^ Pande, Vijay (February 24, 2014).
"Adding a completely new way to fold, directly in the browser". foldingathome.org. Pande Lab, Stanford University. Retrieved February 13, 2015.
^ "NaCL Web Client Shutdown Notice". Folding@Home. Folding@Home. Retrieved August 29,2019.
^ Pande, Vijay (July 7, 2015).
"First full version of our Folding@Home client for Android Mobile phones". Folding@Home. foldingathome.org. Retrieved May 31, 2016.
^ "Folding@Home".
Google Play. 2016. Retrieved May 31, 2016.
^ "Android client overhaul". Folding@home. February 2, 2018. Retrieved July 22, 2019.
^ Lensink MF, Méndez R, Wodak SJ (December 2007). "Docking and scoring protein complexes: CAPRI 3rd Edition". Proteins. 69 (4): 704–18.
doi:
10.1002/prot.21804.
PMID 17918726.
^ Gregory R. Bowman; Vijay S. Pande (2009). "Simulated tempering yields insight into the low-resolution Rosetta scoring function". Proteins: Structure, Function, and Bioinformatics. 74 (3): 777–88.
doi:
10.1002/prot.22210.
PMID 18767152.
^ G. R. Bowman and V. S. Pande (2009). Hofmann, Andreas (ed.).
"The Roles of Entropy and Kinetics in Structure Prediction". PLOS ONE. 4 (6): e5840.
Bibcode:
2009PLoSO...4.5840B.
doi:
10.1371/journal.pone.0005840.
PMC 2688754.
PMID 19513117.
^ Gen_X_Accord, Vijay Pande (June 11, 2006).
"Folding@home vs. Rosetta@home".
Rosetta@home forums.
University of Washington.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved September 20, 2012.
^ Vijay Pande (October 13, 2011).
"Comparison between FAH and Anton's approaches". Folding@home.
typepad.com.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved February 25, 2012.
^
Jump up to: a b c Thomas J. Lane; Gregory R. Bowman; Kyle A Beauchamp; Vincent Alvin Voelz; Vijay S. Pande (2011).
"Markov State Model Reveals Folding and Functional Dynamics in Ultra-Long MD Trajectories". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 133 (45): 18413–9.
doi:
10.1021/ja207470h.
PMC 3227799.
PMID 21988563.
^ David E. Shaw; et al. (2009). Millisecond-scale molecular dynamics simulations on Anton. Proceedings of the Conference on High Performance Computing Networking, Storage and Analysis. pp. 1–11.
doi:
10.1145/1654059.1654099.
ISBN 978-1-60558-744-8.
^ David E. Shaw; et al. (2010). "Atomic-Level Characterization of the Structural Dynamics of Proteins". Science. 330 (6002): 341–346.
Bibcode:
2010Sci...330..341S.
doi:
10.1126/science.1187409.
PMID 20947758.
^ David E. Shaw; Martin M. Deneroff; Ron O. Dror; Jeffrey S. Kuskin; Richard H. Larson; John K. Salmon; Cliff Young; Brannon Batson; Kevin J. Bowers; Jack C. Chao; Michael P. Eastwood; Joseph Gagliardo; J. P. Grossman; C. Richard Ho; Douglas J. Ierardi; et al. (2008). "Anton, A Special-Purpose Machine for Molecular Dynamics Simulation". Communications of the ACM. 51 (7): 91–97.
doi:
10.1145/1364782.1364802.
^ Ron O. Dror; Robert M. Dirks; J.P. Grossman; Huafeng Xu; David E. Shaw (2012). "Biomolecular Simulation: A Computational Microscope for Molecular Biology".
Annual Review of Biophysics. 41: 429–52.
doi:
10.1146/annurev-biophys-042910-155245.
PMID 22577825.
^ TJ Lane (Pande lab member) (June 6, 2011).
"Project 7610 & 7611 in Beta". Folding@home.
phpBB Group.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved February 25, 2012.(
registration required)
^ Pande lab.
"Project 7610 Description". Folding@home.
Archived from the original on September 21, 2012. Retrieved February 26, 2012.
Sources[
edit]
Folding@home (n.d.e),
"About", Folding@home, retrieved April 26, 2020
Mims, Christopher (November 8, 2010),
"Why China's New Supercomputer Is Only Technically the World's Fastest", Technology Review, MIT, archived from
the original on September 21, 2012, retrieved September 20, 2012
Pande, Vijay S. (November 10, 2008),
"Re: ATI and NVIDIA stats vs. PPD numbers", Folding Forum, the fifth post from below, archived from
the original on September 21, 2012, retrieved April 26, 2020
External links[
edit]

Wikimedia Commons has media related to
Folding@home.
Official website 
Listen to this article (
info/dl)

MENU
0:00

This audio file was created from a revision of the article "Folding@home" dated 2014-10-07, and does not reflect subsequent edits to the article. (
Audio help)
More spoken articles
show
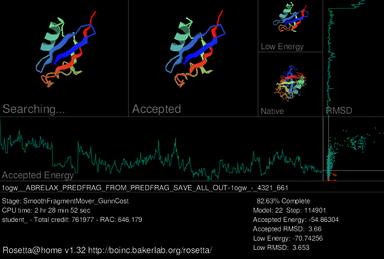
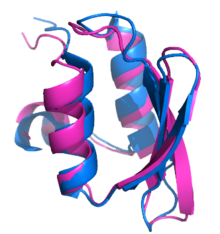














 Wikimedia Commons has media related to
Wikimedia Commons has media related to